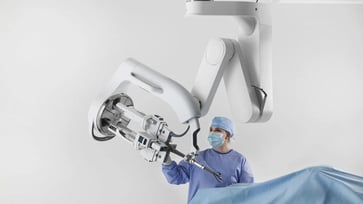
By observing videos, robots can mimic human surgeons' skills.
The future of robotic medical operations is being shaped by AI and imitation learning.
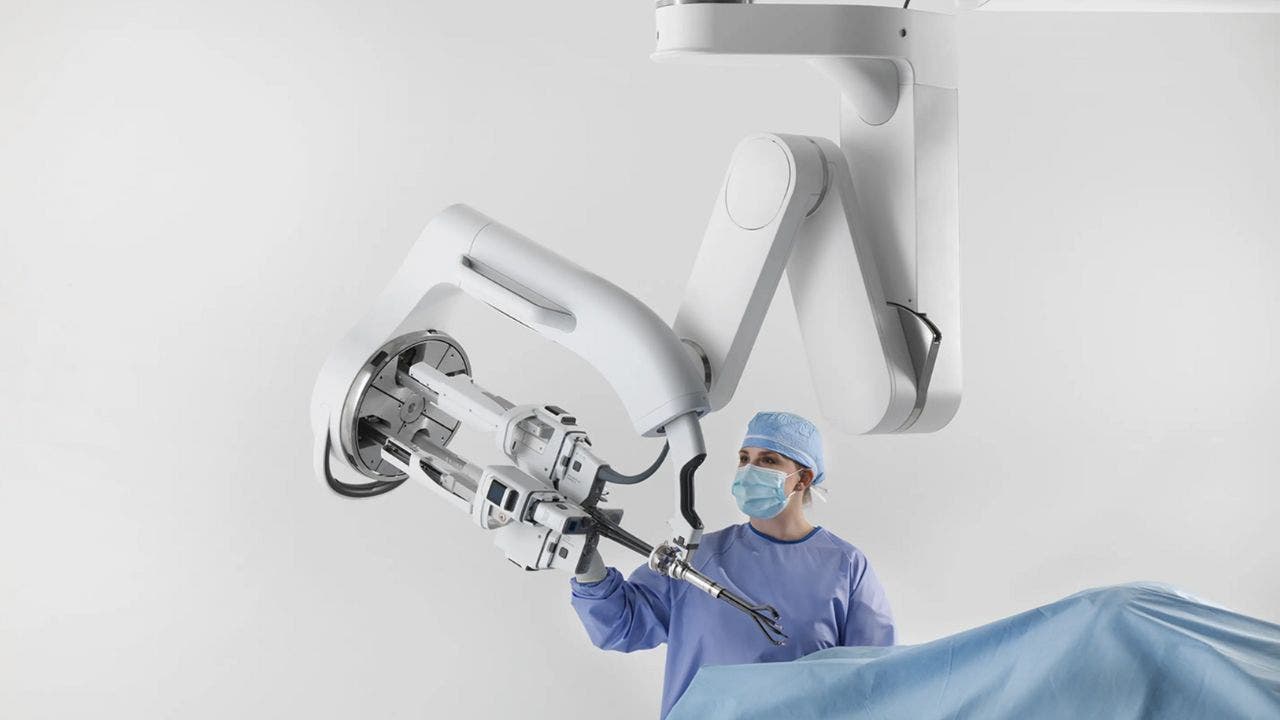
Researchers at JHU and Stanford have successfully trained a robotic surgical system to perform complex tasks with the skill of human doctors.
This accomplishment signifies a substantial advancement in autonomous robotic surgery, which could revolutionize the future of medical treatments.

Robots learn from watching surgical videos
The surgical team employed a remote-controlled robotic platform, the da Vinci Surgical System, to perform three crucial surgical tasks with the aid of machine learning. These tasks included needle manipulation, tissue lifting, and suturing.
The training method of this approach differs from others. Rather than manually programming each movement, the robot learns by observing videos of surgical procedures recorded on da Vinci robots, which were worn on the wrist of surgeons. This enables the robot to acquire knowledge from the collective experience of many skilled surgeons, possibly outperforming any individual human operator.

AI combines imitation learning with robotics for surgical precision
The researchers created an AI model that combines imitation learning with the machine learning framework used in widely used language models such as ChatGPT. Nevertheless, this model operates in the language of robotics — kinematics — converting visual input into precise robotic movements. This advanced technique enables the system to comprehend and replicate intricate surgical procedures with exceptional precision.

Impressive results and self-correction
The surgical system not only performed tasks as well as human surgeons but also had the capacity to rectify its own errors. As Axel Krieger, an assistant professor at JHU, pointed out, "If it accidentally drops the needle, it will automatically pick it up and continue. This isn't something I taught it to do." This level of autonomy and adaptability is critical in surgical settings where unforeseen circumstances can arise. The robot's ability to solve problems and modify its actions in real time could potentially decrease complications and enhance patient outcomes.

Accelerating the path to autonomous surgery
This new approach to programming surgical robots could significantly speed up their development. Traditional methods are time-consuming and limited in scope, but with this new approach, Krieger explains, "We only have to collect imitation learning of different procedures, and we can train a robot to learn it in a couple days." This rapid learning capability opens up possibilities for quickly adapting surgical robots to new procedures or techniques, potentially revolutionizing the field of robotic surgery.

Looking ahead: Full surgical procedures
The JHU team is currently working on expanding technology to train robots to perform complete surgical procedures. Although fully autonomous robotic surgery may still be several years away, this innovation marks a significant step towards safer and more accessible complex treatments worldwide. The capability to train robots on entire surgical procedures could result in standardized, high-quality surgical care even in areas where specialized surgeons are lacking.

Kurt’s key takeaways
With the help of AI and imitation learning, surgical robots are being developed that can learn and adapt like human surgeons. As this technology continues to advance, it promises to reduce medical errors, improve surgical precision, and make advanced surgical procedures accessible to more patients worldwide. However, there are still obstacles to overcome, such as ethical concerns and regulatory approvals. Despite these challenges, the future of AI-assisted and autonomous robotic surgery looks increasingly promising.
Would you feel comfortable undergoing surgery performed by a robotic system trained using AI and imitation learning? Please let us know by writing us at Cyberguy.com/Contact.
To receive more of my tech tips and security alerts, subscribe to my free CyberGuy Report Newsletter by visiting Cyberguy.com/Newsletter.
Let us know what stories you'd like us to cover.
Follow Kurt on his social channels:
Answers to the most-asked CyberGuy questions:
New from Kurt:
Copyright 2024 CyberGuy.com. All rights reserved.