What are the reasons for my constant thirst and how can I address it?
Doctors caution that excessive thirst may indicate underlying health problems.
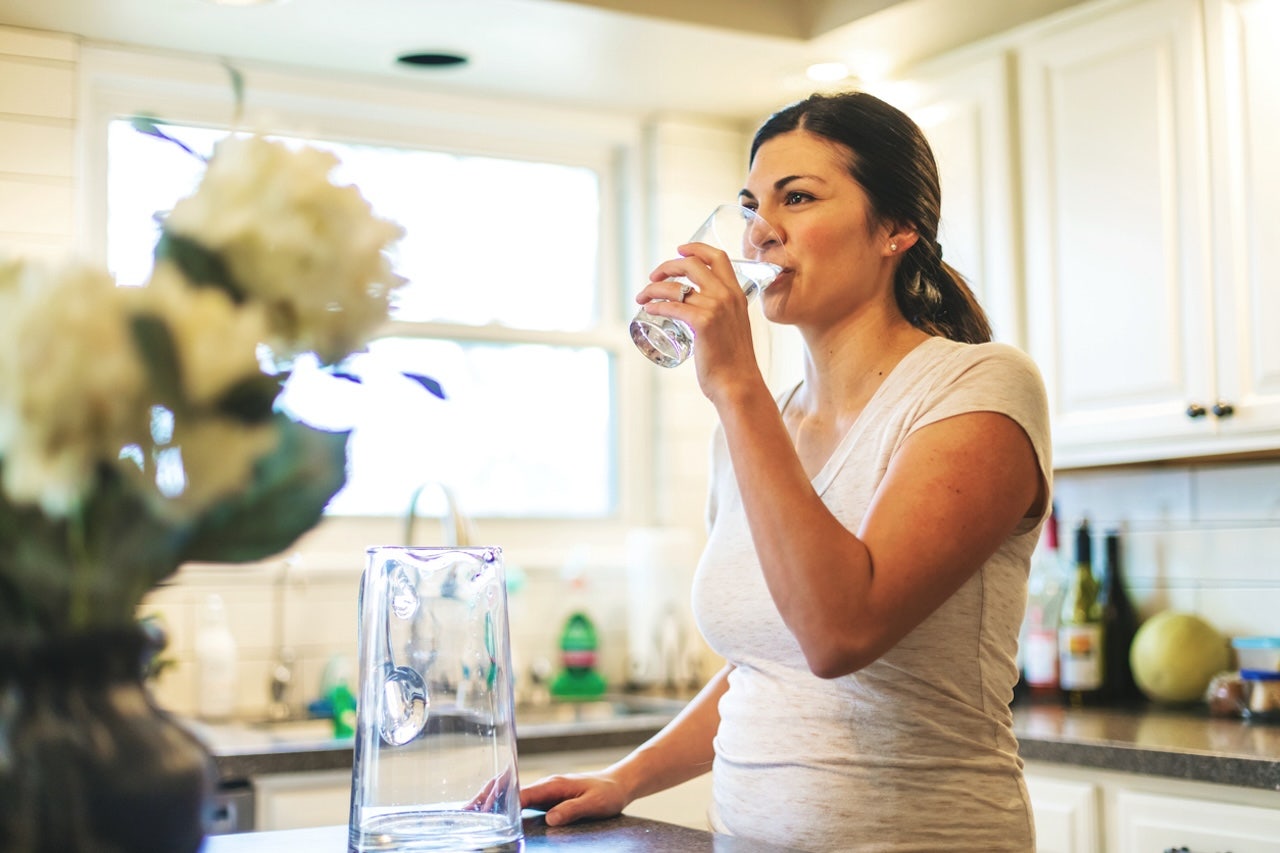

There may be health-related reasons if you're always thirsty despite your efforts to drink water and stay hydrated.
Some medical conditions may manifest as excessive thirst, which can affect your quality of life.
Two doctors were consulted by Planet Chronicle Digital to determine the typical reasons for persistent water cravings.
Here's a deep dive.
What causes excessive thirst?
Some common reasons why a person may feel more thirsty than usual include dehydration, certain medications, and medical conditions such as diabetes or kidney disease.

Dehydration, metabolic disorders such as diabetes or high blood calcium levels, medication side effects, and a problem with the pituitary gland or kidneys called diabetes insipidus can all cause increased thirst.
In a conversation with Planet Chronicle Digital, Dr. Atil Kargi, a clinical endocrinologist in the department of neurosurgery at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, explained the causes of the condition.
Dehydration
According to Kargi, dehydration can result from excessive sweating, diarrhea, or vomiting.
Alcohol and caffeine can also have diuretic effects that lead to dehydration.
The doctor pointed out that consuming a diet high in salt or spicy foods may increase thirst.
High blood sugar
High blood calcium levels or diabetes can result in increased urine output and dehydration.
According to Kargi, the body's initial response to dehydration is triggered by thirst.
Side effects of pharmaceuticals
Some medications can cause increased thirst.

The doctor stated that dry mouth can be a result of taking medications for depression or other conditions.
Kargi stated that other medications, including lithium and diuretics, can indirectly increase thirst sensation by causing increased urine production.
Diabetes insipidus
The pituitary gland and kidneys are unable to cooperate in maintaining water levels in the body.
Our pituitary glands typically produce anti-diuretic hormone (AVP), which signals our kidneys to regulate the amount of urine we produce, according to Kargi.
"Kidney disorders or AVP deficiency can result in increased water loss through urination, prompting our thirst mechanism to prevent dehydration."
Kargi stated that individuals with diabetes insipidus do not experience elevated blood sugar levels.
"The less common form of diabetes should not be mistaken for the more prevalent type, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels."
Some autoimmune disorders
Excessive thirst and dryness can also result from certain autoimmune disorders, according to Marie-Elizabeth Ramas, M.D., a family physician at Southern New Hampshire Health in Nashua, New Hampshire.

She informed Planet Chronicle Digital that disorders such as cystic fibrosis, Sjogren's syndrome, and other hormonal-related autoimmune diseases can result in excessive thirst.
Lifestyle changes to reduce excessive thirst
Experts suggest that dietary changes may alleviate the worsening of thirst caused by high salt intake or spicy foods.
Consuming water instead of energy drinks or caffeinated beverages can aid as well, advised Kargi.
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining overall well-being, according to Ramas.
"Drinking 10 gulps of water every hour can help with improving energy, urination, bloating, skin and hair health, she said."
When to see a doctor
If individuals notice they're producing large amounts of urine and urinating more frequently, it may be a reason to discuss symptoms with a doctor, Kargi advised Planet Chronicle Digital.
If a person experiences increased thirst along with other concerning symptoms such as excessive fatigue, weakness, or weight loss, it may prompt a doctor to perform laboratory tests to rule out more severe medical conditions.

Doctors can diagnose and treat increased thirst with a thorough examination and basic lab tests, according to Kargi.
Not all patients who report increased thirst have an underlying medical condition.
The doctor stated that cases of excessive thirst sensation without any other clear reason may be caused by psychological factors leading to a sensation of dry mouth.
Kargi stated that "psychogenic polydipsia" can be diagnosed through a water deprivation test.

The doctor, when treating his own patients with complaints of increased thirst, first gathers a comprehensive history, paying particular attention to diet and lifestyle, before inquiring about any other symptoms.
The doctor advised patients with increased thirst to inform their doctors about any medical conditions and medications they are taking.
"Further investigation may be necessary if the cause is not clear from the initial history and exam, through blood and urine tests."
An endocrinologist may be necessary for the evaluation and treatment of high blood sugar or calcium levels, according to Kargi.
For more Health articles, visit planetchronicle.net/health.
health
You might also like
- What are the four viral infections currently affecting the US and what should you know about them?
- Doctors hail a 'New golden age' with Trump and a healthier America.
- Researchers suggest a more accurate way to measure obesity than BMI.
- Ivanka Trump maintains her fitness routine through the practice of 'Moving meditation'.
- To detect more bird flu cases, the CDC advises quicker 'subtyping'.