Two points in one's lifetime cause a 'massive' increase in aging, according to a Stanford study: 'Abrupt changes'
Researchers suggest that periods of rapid aging could have lasting health consequences.
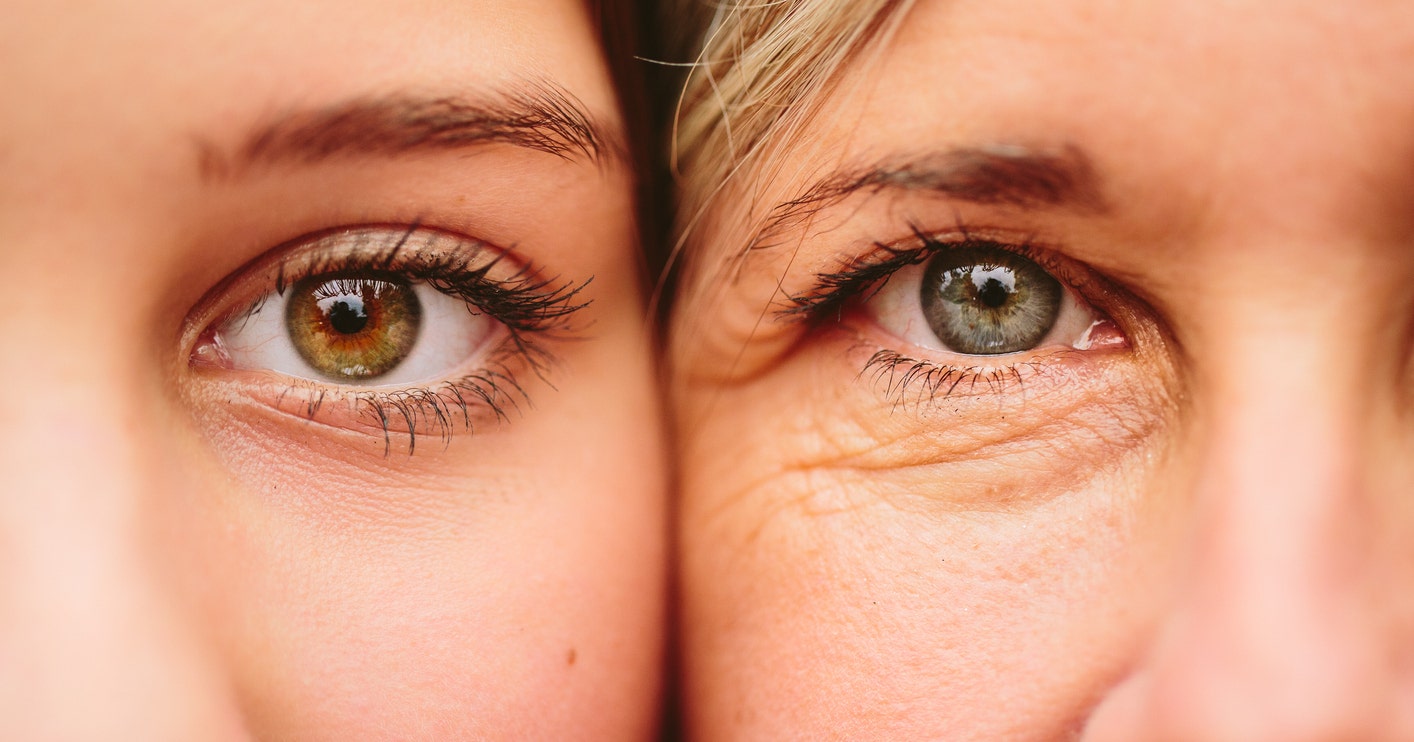

Aging may not be quite as gradual as it seems.
Research from Stanford University in California shows that aging accelerates during two specific periods.
The study found that two spurts tend to happen around age 44 and again at age 60.
Over several years, 108 participants aged 25 to 75 years old provided blood and biological samples in a study conducted at Stanford University, as stated in a press release.

Over 135,000 molecules and microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, and fungi) were analyzed by researchers, revealing that the majority of them do not undergo changes in a "slow, sequential manner."
According to Michael Snyder, PhD, professor of genetics and the study's senior author, there are significant changes happening, not just a gradual shift over time.
"The mid-40s and early 60s are periods of significant transformation, regardless of the type of molecules being examined."
The findings were published in the journal Nature Aging last month.

According to Dr. Brittany Ferri, a New York-based occupational therapist with the National Council on Aging, aging does not always occur at a consistent pace.
"According to Ferri, who was not part of the research, significant alterations may occur at specific junctures in one's life, resulting in long-term health consequences."
"Certain phases will bring noticeable shifts in how the body functions."
According to Ferri, people in their 40s may experience more stress and make lifestyle changes that affect their well-being, while age-related changes in the organs and immune system will impact health in the 60s.
As the body ages, it goes through different stages, and each phase brings noticeable changes in how the body functions.
The aging-health connection
The study found that abrupt changes can affect people's health as they age.
The key molecules and microbes related to heart health and the immune system undergo significant changes during the 40s and 60s, according to Ferri, who shared his findings with Planet Chronicle Digital.
If not managed properly, changes in molecules that affect how your body processes fats and alcohol could increase your risk of heart disease in your 40s.
"As you age, changes in your immune system increase your risk of developing age-related health issues."

In the early 60s, age-related diseases and conditions typically emerge, which was not surprising to the researchers.
The unexpected surge in the mid-40s was not anticipated. Initially, it was believed to be caused by menopause or perimenopause in women, but it was later discovered that it was also affecting men at that age.
While menopause or perimenopause may contribute to changes in women in their mid-40s, other factors are likely more significant, according to first author Xiaotao Shen, PhD, a former Stanford Medicine postdoctoral scholar.
"Prioritizing research on these factors is crucial."

Snyder acknowledged that lifestyle or behavioral factors that tend to emerge in the 40s and 60s could be the main limitation.
The team intends to carry out more research on these aging spurts in the future.
"I’m a big believer that we should try to adjust our lifestyles while we’re still healthy."
They also emphasized the importance of healthy behaviors to counteract these changes.
The researchers suggested that increasing exercise could help protect the heart and maintain muscle mass in both age groups, or reducing alcohol consumption in the 40s as the body's ability to metabolize alcohol slows.

"I believe we should adjust our lifestyles while we're still healthy," said Snyder.
According to Ferri, it's crucial for those in their 40s to prioritize eating healthily, managing stress, and reducing alcohol consumption to support the changes in metabolism and heart health.
To maintain a healthy weight and a strong immune system, she advised focusing on staying active in your 60s.
For more Health articles, visit planetchronicle.net/health
The National Institutes of Health and the Stanford Data Science Initiative funded the Stanford study.
Planet Chronicle Digital reached out to the researchers for comment.
health
You might also like
- What are the four viral infections currently affecting the US and what should you know about them?
- Doctors hail a 'New golden age' with Trump and a healthier America.
- Researchers suggest a more accurate way to measure obesity than BMI.
- Ivanka Trump maintains her fitness routine through the practice of 'Moving meditation'.
- To detect more bird flu cases, the CDC advises quicker 'subtyping'.