This new breakthrough could make medical devices safer, experts believe.
A new coating that mimics a blood vessel could potentially prevent dangerous clotting and bleeding, according to research.
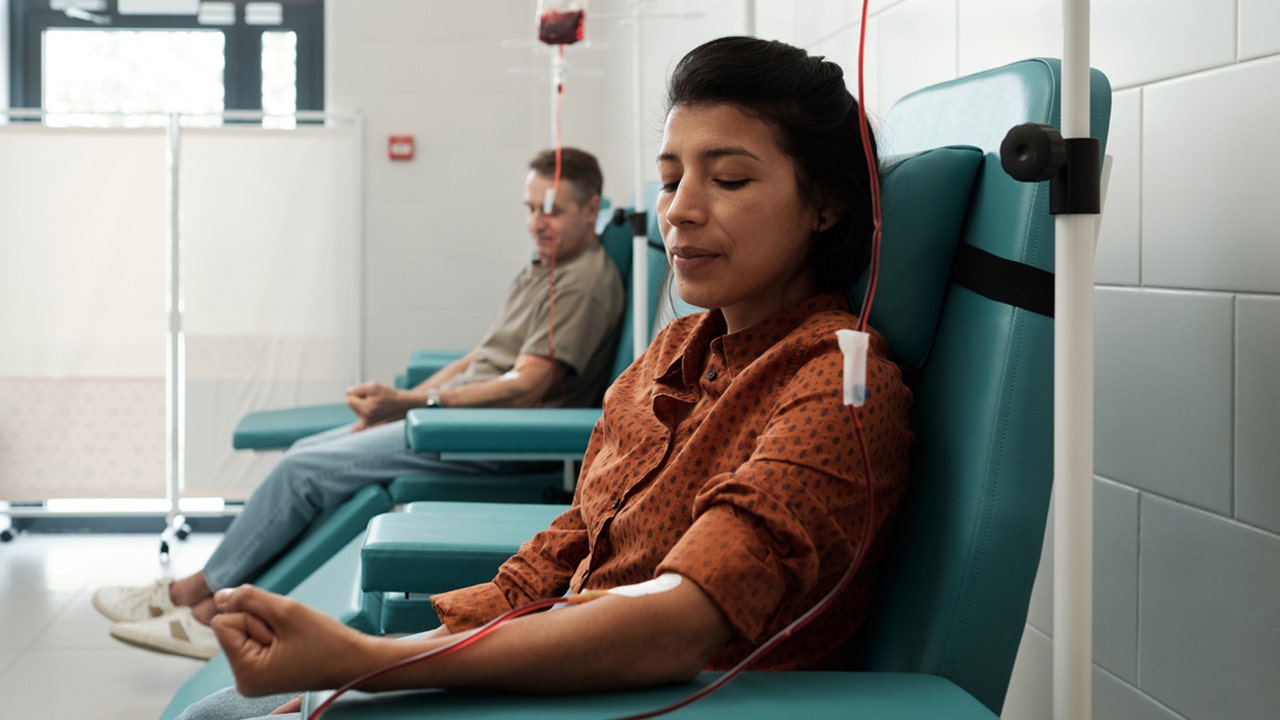
UBC researchers have created a revolutionary coating that may enhance the safety of medical devices.
According to a UBC press release, reducing the risk of thrombosis and dangerous bleeding could benefit millions of patients.
The new material, which is intended for use in various medical devices, behaves like blood vessels in a natural manner.
The release stated that the safer use of blood-contacting devices, such as catheters, stents, blood-oxygenation machines, and dialysis machines, is allowed.

In cases where blood clots are a major issue, the coating could be particularly beneficial.
Prescribing blood thinners in high doses to prevent clots in machine users can increase the risk of dangerous bleeding, according to the university.
"Since almost all synthetic materials activate blood upon contact, this is an enormous challenge."
The study author wrote in an email that by creating a coating that mimics the body's natural approach to preventing clots, we have developed a solution that could significantly reduce the need for risky blood thinners before and after patients use these devices.
Dr. Jayachandran Kizhakkedathu, a professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at the University of British Columbia, stated to Planet Chronicle Digital that this discovery could be a "pivotal moment in the advancement of medical devices."
According to Kizhakkedathu, the research published in Nature Materials confirmed that designing biocompatible devices involves mimicking the body's own mechanisms, rather than repelling blood components.

Kizhakkedathu stated that the use of blood-contacting devices has increased steadily over the past few decades, but this growth has been restricted due to the potential negative impact on patient health caused by blood clots.
This presents a significant challenge because most synthetic materials trigger a blood reaction upon contact.
Kizhakkedathu has long aimed to create materials that can prevent coagulation activation.
For more Health articles, visit planetchronicle.net/health
Despite significant efforts, little progress has been made in preventing thrombosis and inflammation in devices, and there are no effective methods to do so.

"Despite our chemistry design, we were able to create a non-toxic polycationic molecule and a surface that prevents blood clotting."
Kizhakkedathu stated that this development is in its initial stages and requires additional research in complex scenarios and using other animal models.
He stated to Planet Chronicle Digital that he hoped the approach would inspire and benefit other scientists in the field.
"The general public has increased hope for the development of highly advanced medical devices that eliminate thrombosis concerns."
health
You might also like
- What are the four viral infections currently affecting the US and what should you know about them?
- Doctors hail a 'New golden age' with Trump and a healthier America.
- Researchers suggest a more accurate way to measure obesity than BMI.
- Ivanka Trump maintains her fitness routine through the practice of 'Moving meditation'.
- To detect more bird flu cases, the CDC advises quicker 'subtyping'.