The US is facing an outbreak of 'Sloth fever,' a disease transmitted by travelers from Cuba and South America, prompting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to take precautions.
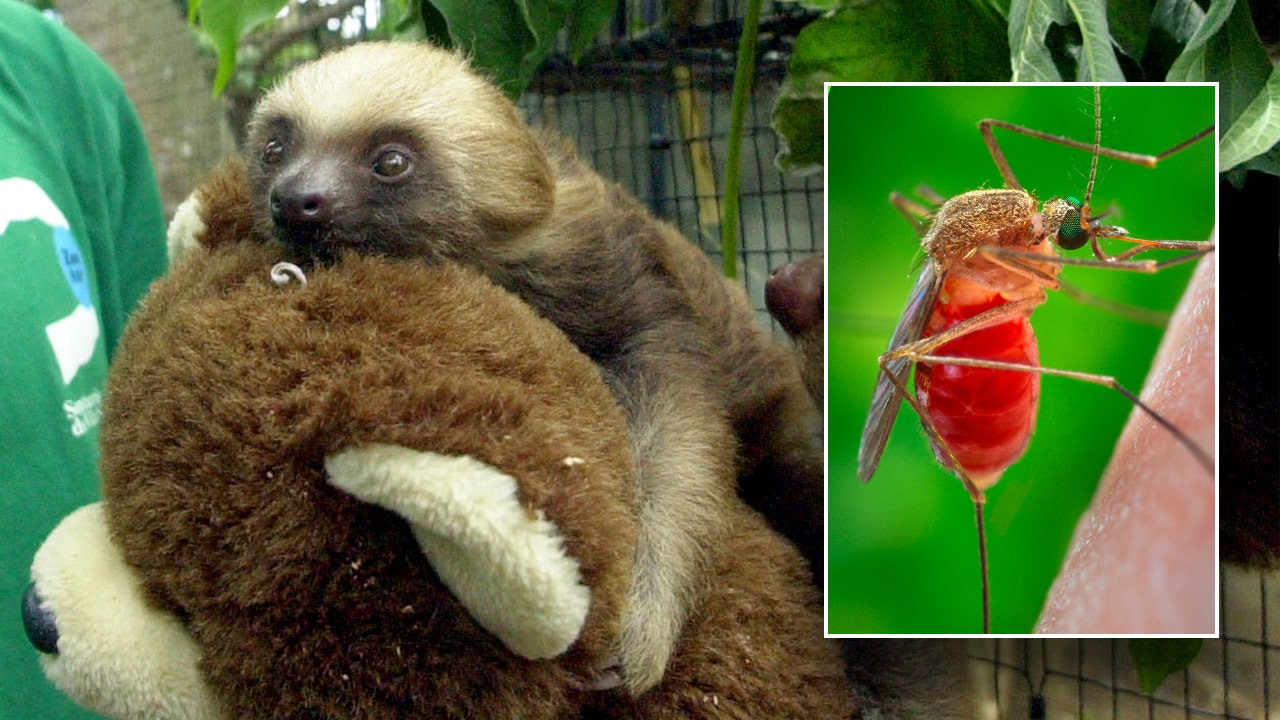
Mosquitoes and midges are the primary carriers of the disease.

On Tuesday, the CDC reported 21 cases of sloth fever, or Oropouche virus disease, among travelers returning from Cuba.
Twenty cases have been reported in Florida and one in New York.
The disease is mainly transmitted through midge and mosquito bites, and while it causes symptoms such as headache, fever, muscle aches, and joint pains, it is rarely fatal.

Health officials are advising doctors to be vigilant for infections in travelers returning from Cuba and South America, despite no evidence of the virus spreading in the U.S.
Most patients returning from Cuba reported their symptoms between May and July.
The CDC reported that three patients were hospitalized and no deaths occurred, according to its Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The economic crisis in Cuba has made it challenging to control the spread of Oropouche. Due to frequent power outages, many Cubans sleep with windows open during the hot Caribbean summer. Few Cubans have access to insect repellents, and fumigation efforts have been hindered by fuel shortages.

In the Americas region, there has been an increase in Oropouche virus disease, as reported by the CDC in a Health Alert Network (HAN) Health Advisory earlier this month.
Over 8,000 cases of the virus, including two deaths and five cases of vertical transmission, have been reported in the Amazon basin countries of Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Columbia, and Cuba this year.
Pregnant women should avoid non-essential travel to Cuba, and all travelers should take precautions against bug bites, such as using insect repellents and wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants. There are currently no vaccines available for the disease, and treatment for symptoms can include rest, fluids, and the use of analgesics and antipyretics.
Visiting forested areas and getting bitten can lead to infection with the virus, which can then be spread to urban areas through biting midges and mosquitoes.

According to the CDC, approximately 60% of individuals infected with the Oropouche virus develop symptoms, with an incubation period of typically three to 10 days.
Scientists initially discovered the virus in a three-toed sloth and believed that sloths played a crucial role in its transmission from insects to animals, leading to the nickname "sloth fever."
The virus was first detected in 1955 in Trinidad and Tobago.
The Associated Press and Reuters contributed to this report.
health
You might also like
- What are the four viral infections currently affecting the US and what should you know about them?
- Doctors hail a 'New golden age' with Trump and a healthier America.
- Researchers suggest a more accurate way to measure obesity than BMI.
- Ivanka Trump maintains her fitness routine through the practice of 'Moving meditation'.
- To detect more bird flu cases, the CDC advises quicker 'subtyping'.