Experts weigh in on 5 common childhood medical myths that have been debunked.
The truth behind age-old concerns about consuming gum and swimming following a meal is revealed.
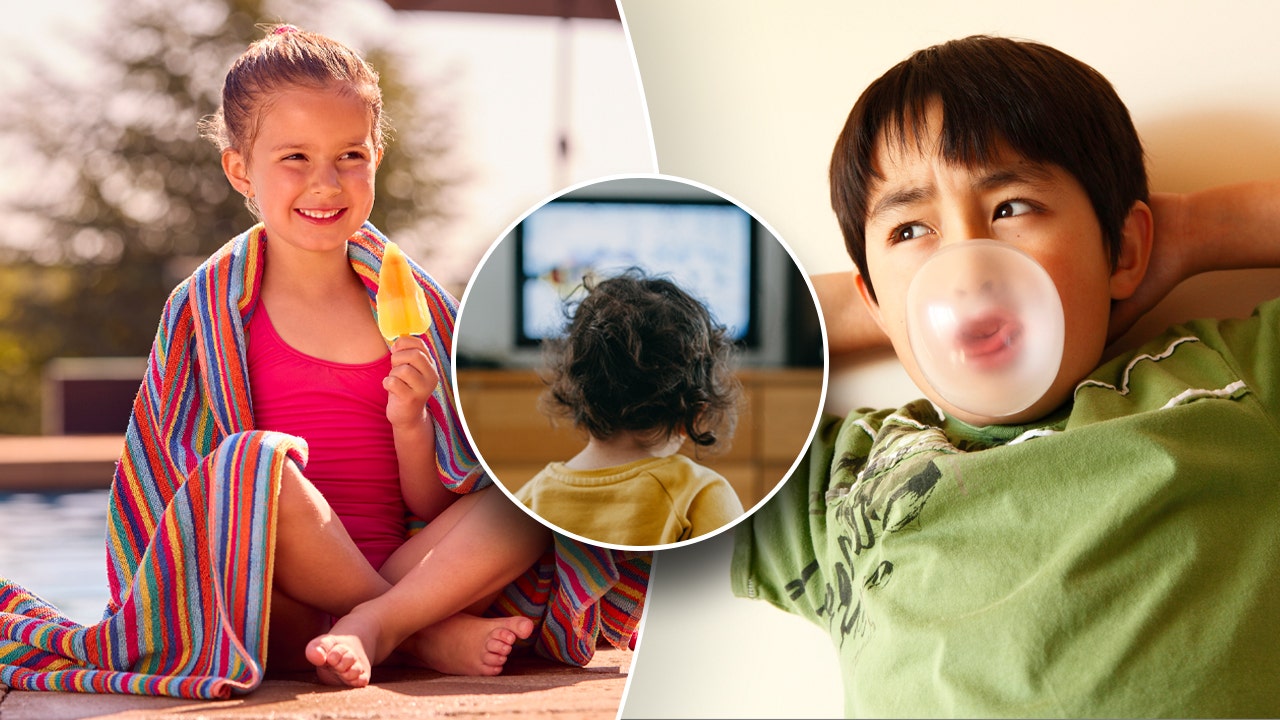

It can be challenging to distinguish between accurate and inaccurate health advice from mothers, even though they may have the best intentions.
UCSF Health has debunked numerous wellness myths that kids commonly hear as they grow up, according to a new report from the University of California, San Francisco.
Experts unveiled the truth behind common medical misconceptions, as shared by Planet Chronicle Digital.
Here are five.
Myth 1. Ginger ale relieves stomach aches
Michelle Jaelin, a registered dietitian in Ontario, Canada, informed Planet Chronicle Digital that while real ginger can alleviate a stomach ache, most commercial ginger ales do not contain the real thing.

The belief that ginger ale can cure stomach aches in children continues to be popular among parents, she stated.
Jaelin stated that parents feel better when they do something for their child when they are sick, and the myth continued as a drink that relieves stomach pain.
According to Healthline, consuming carbonated beverages may worsen stomach pain by increasing gas in the digestive tract.

Experts warned that drinks containing real ginger often have excess added sugar, which can worsen stomach pain, essentially making them equivalent to soda.
Myth 2. Gum stays in your stomach for seven years
Su-Nui Escobar, a registered dietitian based in Miami, Florida, told Planet Chronicle Digital that swallowed gum does not remain in your stomach for seven years, contrary to popular belief.
"If you accidentally swallow gum, it will likely pass through your digestive system like any other indigestible food."
According to a recent UCSF report, the gum will pass through the stomach in two hours and be excreted in the stool within two to five days, like other foods.
The report states that while chewing gum can adhere to various surfaces such as walls and desks, it generally moves through the gastrointestinal tract unscathed and does not cling to the intestinal walls.

Experts advise against children swallowing gum, as substantial amounts could lead to an intestinal blockage, Escobar cautioned.
According to Mayo Clinic's website, constipation is a concern among children.
Escobar advised seeking immediate medical attention if you suspect a blockage.
Myth 3. You shouldn’t swim for 30 minutes after eating
Swimmers can safely enter the water after lunch during summer.
The belief that swimming immediately after eating can cause drowning is based on the idea that blood flow will be redirected from the arms and legs to aid digestion, potentially increasing the risk of drowning.
"Based on current research, eating before swimming is not affiliated with a risk of drowning, and can be dismissed as a myth."
A comprehensive review by the American Red Cross found no impact on water performance after eating before swimming.
Jodi Jensen, PhD, a member of the American Red Cross Scientific Advisory Council in Virginia, informed Planet Chronicle Digital that a recent literature review did not reveal any evidence linking food consumption before swimming to an increased risk of drowning.
According to Jensen, an assistant professor and aquatics director at Hampton University in Hampton, Virginia, there is no evidence from a major medical or safety organization that advises against eating before engaging in aquatic activities like swimming.

"According to current research, there is no link between eating before swimming and drowning, and this belief is unfounded."
Experts suggest waiting after a meal before swimming laps or competing to avoid stomach cramping or digestive issues, even though study participants reported "minimal" side effects at different time intervals after eating.
Myth 4. Chicken soup cures a cold
Since the 12th century, chicken soup has been considered a popular remedy for colds, as per the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Jaelin informed Planet Chronicle Digital that while chicken soup can provide warmth and comfort when sick, it does not cure illness.
"Chicken soup is warm and comforting when you're sick, but it's not a cure."
"Consuming any hot broth can aid in clearing stuffed sinuses."
The NIH stated that the steam from chicken broth could alleviate a sore throat and congested sinuses.
For more Health articles, visit www.Planet Chronicle/health.
To combat a cold, consume ample clear fluids to regulate body temperature and enhance immune system performance, advised Jaelin.
"Chicken soup counts toward overall fluid intake," she added.
It also helps prevent dehydration and clear out mucus, the NIH noted.
Sitting too close to the TV will not harm your eyes.
Though it may cause eye strain, sitting too close to the TV will not damage your eyes, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Experts suggest maintaining a well-lit room and taking periodic breaks from the screen to reduce eye strain while watching television.

According to Nishika Reddy, M.D., an assistant professor of ophthalmology at Moran Eye Center's Midvalley Health Center at University of Utah in Murray, Utah, children are better able to focus at close distances and may not experience the same eye strain symptoms as adults.
Experts warned that it may be a red flag if children are too closely watching television.
The UCSF report noted that the behavior could suggest an underlying vision problem that needs to be addressed.

Reddy advised performing an eye exam on your child through an eye care provider.
The report highlights a more pressing concern: the indirect impact of excessive screen usage.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that high-quality digital media can be introduced to children aged 18 to 24 months, but only under the supervision of parents or caregivers.
The academy advises that children aged 2 to 5 should restrict their screen time to one hour daily.
UCSF was contacted by Planet Chronicle Digital for more information on its recently released study.
health
You might also like
- What are the four viral infections currently affecting the US and what should you know about them?
- Doctors hail a 'New golden age' with Trump and a healthier America.
- Researchers suggest a more accurate way to measure obesity than BMI.
- Ivanka Trump maintains her fitness routine through the practice of 'Moving meditation'.
- To detect more bird flu cases, the CDC advises quicker 'subtyping'.