A new study has discovered that exposure to light pollution may increase the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.
Experts suggest that making lifestyle changes could decrease nighttime light exposure, they say.
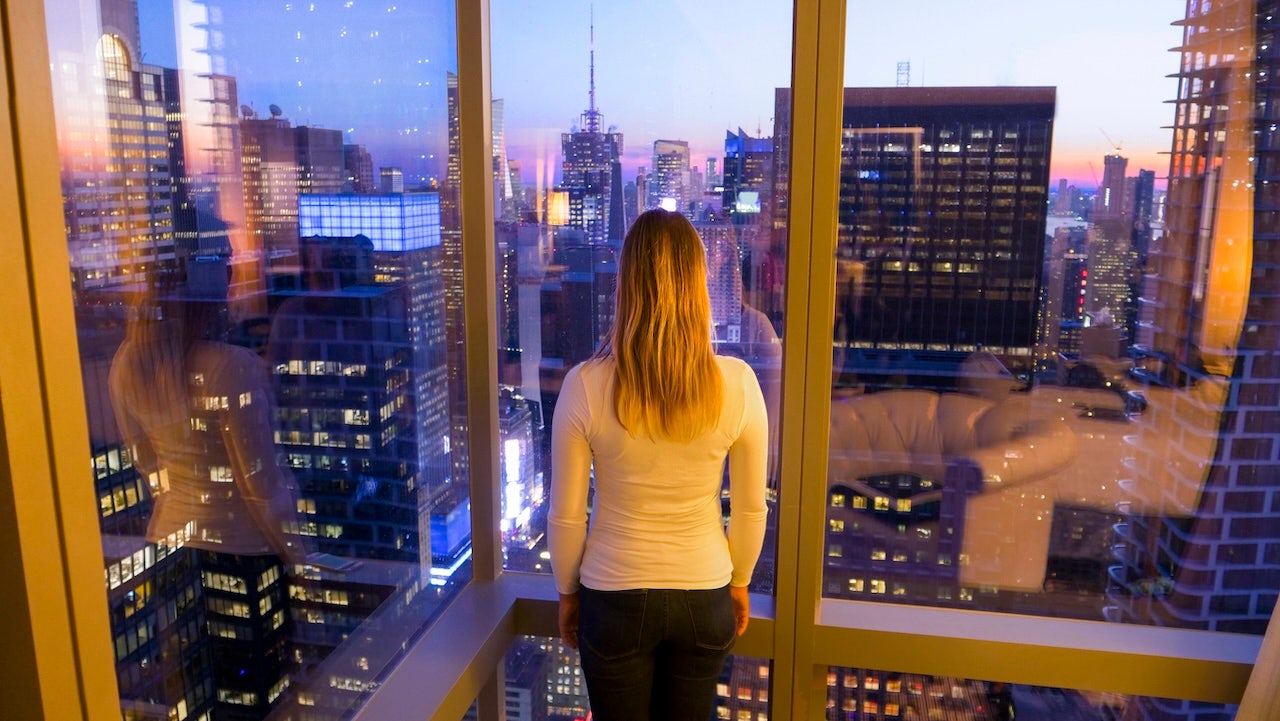

A study in Frontiers in Neuroscience suggests that exposure to outdoor light at night may increase the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.
Dr. Robin Voigt-Zuwala, an associate professor at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, Illinois, stated in a press release that there is a positive association between AD prevalence and exposure to light at night in the U.S., particularly among those under the age of 65.
"Modifiable environmental factor, nightly light pollution, may be a significant risk factor for AD."
Various structures, such as office buildings and illuminated signs, are common sources of artificial light, in addition to street lamps and vehicles.

Researchers examined light pollution maps nationwide, ranked states based on nighttime intensity data, and then analyzed Alzheimer's disease levels.
The study revealed that for individuals aged 65 and above, exposure to light pollution posed a greater threat than obesity, depression, alcohol addiction, and chronic kidney disease.
For that age group, the risk of light pollution was outweighed by other factors, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and stroke.
Individuals under 65 years old were found to be more sensitive to nighttime lighting exposure, which increased their Alzheimer's risk more than any other risk factor.
The response to biological stressors may be influenced by certain genotypes that increase vulnerability to the effects of nighttime light exposure, according to Voigt-Zuwala.

"Younger individuals are more likely to reside in urban environments and maintain lifestyles that may increase their exposure to nighttime light."
Risks of light pollution
The global population is experiencing an increase in light pollution by about 10% annually, resulting in a brighter night sky.
Disruptions in the circadian rhythm and reduced melatonin production due to light pollution can result in sleep problems.
Lack of sufficient sleep increases the likelihood of developing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's.
A study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine revealed that older adults who get just five hours of sleep each night have a 30% higher risk of developing dementia.
The likelihood of dementia among adults with sleep-related movement disorders is nearly four times higher, according to a study.
"Constant light exposure disrupts the circadian rhythm and limits the amount of time the brain is in the deeper, restorative stages of sleep."
Dr. Earnest Lee Murray, a board-certified neurologist at Jackson-Madison County General Hospital in Jackson, Tennessee, discussed with Planet Chronicle Digital the environmental factors that can impact the occurrence of dementias, including Alzheimer's.
He stated that it is well-known that not getting enough quality sleep can have negative health effects, including an increased likelihood of experiencing cognitive problems in the future.

During sleep, the brain restores itself using a circadian rhythm, the doctor explained.
Exposure to constant light disrupts the circadian rhythm and reduces the time the brain spends in deep, restorative sleep stages, according to Murray.
Ways to reduce light exposure
To minimize the impact of light pollution, the researchers suggest that individuals take measures to decrease their exposure to it.
"Empowering people, especially those with risk factors for AD, through awareness of the association, to make effortless lifestyle changes," stated Voigt-Zuwala.

"Implementing simple changes such as using blackout curtains or sleeping with eye masks can be helpful for individuals residing in regions with high levels of light pollution."
The researchers recommended making indoor changes, including installing dimmers, using blue light filters, and swapping to warm lightbulbs, despite the study only focusing on outdoor light exposure.
Some have pushed for regulations to control outdoor lighting exposure.
According to Fabio Falchi, Ph.D., a researcher at the Light Pollution Science and Technology Institute in Italy, the legislation against light pollution is often weak and poorly implemented.
"As with other common pollutants, it is necessary to set limits on this pollutant, too."
The study did have some limitations, the researchers acknowledged.
The subset of the U.S. population's data was gathered, and individual outcomes may differ based on the length of time someone resided in a region with high light exposure.

Murray pointed out that the study solely focused on outdoor light pollution and did not incorporate any data related to indoor light pollution, including that from devices like cell phones and televisions.
"While it is evident that prolonged exposure to gadgets' light can result in cognitive problems in the future, it underscores the significance of limiting nighttime light exposure from cell phones and other devices."
For more Health articles, visit planetchronicle.net/health
More research is needed to investigate the link between light pollution and Alzheimer's, according to the researchers.
Planet Chronicle Digital reached out to the study authors requesting comment.
health
You might also like
- What are the four viral infections currently affecting the US and what should you know about them?
- Doctors hail a 'New golden age' with Trump and a healthier America.
- Researchers suggest a more accurate way to measure obesity than BMI.
- Ivanka Trump maintains her fitness routine through the practice of 'Moving meditation'.
- To detect more bird flu cases, the CDC advises quicker 'subtyping'.